Compendium Review Unit 1 Major Topic 2
I. Patterns of Chromosome Inheritance
A. Cell Cycle
1.karyotype
2. cycle
B. Mitosis
1.overview
a. prophase
b. metaphase
c. anaphase
d. telephase
2. cytokinesis
C. Meiosis
1. stages
D. Comparison of meiosis and mitosis
1. spermatogenesis and oogenesis
E. Chromosome Inheritance
1. changes in number
2. chromosomal disorders
3. changes in structure
II. Cancer
A. characteristics of cancer cells
1. genetic disease
2. types of cancer
a. carcinomas
b. sarcomas
c. leukemias
d. lymphomas
B. Causes and Prevention
1. heredity
2. environmental carcinogens
3. dietary
C. Diagnosis
1. warning signs
2. screening tests
3. tumor marker tests
4. genetic tests
D. Treatment of Cancer
1. surgery
2. radiation
3. chemotherapy
4. newer therapies
III. Patterns of Genetic inheritance
A. Genotype and phenotype
B. One and two trait inheritance
1. forming gametes
2. one trait crosses
3. two trait crosses
4. family pedigrees for genetic disorders
5. genetic disorders
C. Beyond Simple Inheritance Patterns
1. polygenic inheritance
2. incomplete dominance and codominance
3. multiple allele inheritance
D. sex linked inheritance
1. x-linked alleles
2. x-linked disorders
IV. DNA Biology and Technology
A.DNA and RNA structure and function
1. structure of DNA
2. replication of DNA
3. structure and function of RNA
a. ribosomal RNA
b. messenger RNA
c. transfer RNA
B. Gene Expression
1. structure and function of proteins
2. gene expression
3. transcription
4. translation
5. regulation
C. Genomes
1. sequence of human genome
2. functional and comparative genomics
3. proteomics and bioinformatics
4. modifying human genome
D. DNA Technology
1. isolating and cloning genes
2. cloning specific DNA sequences
3. biotechnology products
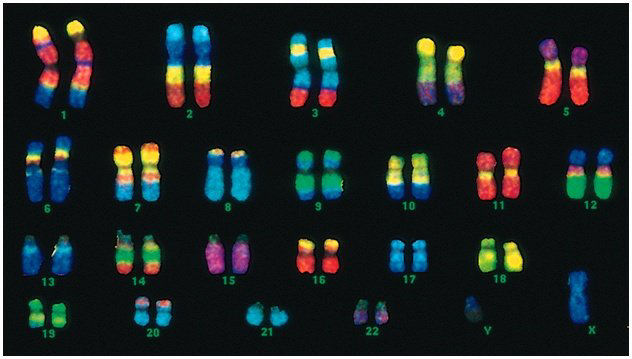
Humans have a total of 46 chromosomes. They are paired up, giving us 23 pairs. Twenty two of these pairs are called autosomes and control traits that have nothing to do with a person's gender. The other pair is called the sex chromosomes because they do determine gender. Males are X and Y, and females are X and X.
picture is of human chromosomes
Karyotypes tell us about cells in the body. A normal body cell has all forty six chromosomes. Mitosis is the process that ensures that every cell has this number. When cells divide, each chromosome is composed of two parts that are identical, called sister chromatids. These contain a DNA double helix. The chromatids are connected at a place called the centromere until the phase of mitiosis in whcih it splits.
The cell cycle has two parts. These are called interphase and cell division. Most of the cell cycle is spent in interphase which is broken down into three parts. The organelles carry on their usual functions during this time.

The first stage is known as the G1 stage. The cell doubles its organelles and gathers the materials needed to synthesize DNA. Next is the S stage in which DNA replication occurs, duplicating the chromosomes. In the G2 stage, the cell synthesizes the proteins that are needed for the cell division. After interphase, the cell begins dividing. The first part of this is called M (for mytotic), and cytokinesis. Mitosis is the nuclear division and cytokinesis is division of the cytoplasm. There is a process called apoptosis which is programmed cell death, which occurs to get rid of cells that are dividing when they shouldn't be.
Mitosis is known as duplication division. The nucleus in both of the new cells have the exact same number and types of chromosomes as the cell that divides. The cell that divides is the parent cell, and the daughter cells are the new cells. When mitosis is about to occur, the chromatin in the nucleus becomes condensed. The centrosomes duplicate and then separate forming the poles of the mitotic spindle. There are four phases of mitosis. The first, prophase, visibly indicate that the cell is ready to divide. Spindle fibers begin to appear and the nuclear envelope begins to split apart. The nucleolus disappears. The chromosomes shorten and thicken and spindle fibers attach to the centromeres. In the next phase, metaphase, the spindle occupies where the nucleus was. The chromosomes are at the center, each with two sister chromatids. In anaphase, the third phase, the centromeres divide, followed by the sister chromatids. The diploid chromosomes move toward each pole. Last is telophase which happens when the chromosomes reach the poles. There they once again become chromatin. The spindles disappear and the nuclear envelope reforms. There are now two daughter nuclei. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm and the organelles divide, resulting in each cell being enclosed by its own plasma membrane. The cell cycle is very important to a human's well being. It kicks in to repair injuries, and to help us grow.
The cell that divides is the parent cell, and the daughter cells are the new cells. When mitosis is about to occur, the chromatin in the nucleus becomes condensed. The centrosomes duplicate and then separate forming the poles of the mitotic spindle. There are four phases of mitosis. The first, prophase, visibly indicate that the cell is ready to divide. Spindle fibers begin to appear and the nuclear envelope begins to split apart. The nucleolus disappears. The chromosomes shorten and thicken and spindle fibers attach to the centromeres. In the next phase, metaphase, the spindle occupies where the nucleus was. The chromosomes are at the center, each with two sister chromatids. In anaphase, the third phase, the centromeres divide, followed by the sister chromatids. The diploid chromosomes move toward each pole. Last is telophase which happens when the chromosomes reach the poles. There they once again become chromatin. The spindles disappear and the nuclear envelope reforms. There are now two daughter nuclei. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm and the organelles divide, resulting in each cell being enclosed by its own plasma membrane. The cell cycle is very important to a human's well being. It kicks in to repair injuries, and to help us grow.
Meiosis is known as reduction division, involving four daughter cells.
Mitosis is known as duplication division. The nucleus in both of the new cells have the exact same number and types of chromosomes as the cell that divides.
 The cell that divides is the parent cell, and the daughter cells are the new cells. When mitosis is about to occur, the chromatin in the nucleus becomes condensed. The centrosomes duplicate and then separate forming the poles of the mitotic spindle. There are four phases of mitosis. The first, prophase, visibly indicate that the cell is ready to divide. Spindle fibers begin to appear and the nuclear envelope begins to split apart. The nucleolus disappears. The chromosomes shorten and thicken and spindle fibers attach to the centromeres. In the next phase, metaphase, the spindle occupies where the nucleus was. The chromosomes are at the center, each with two sister chromatids. In anaphase, the third phase, the centromeres divide, followed by the sister chromatids. The diploid chromosomes move toward each pole. Last is telophase which happens when the chromosomes reach the poles. There they once again become chromatin. The spindles disappear and the nuclear envelope reforms. There are now two daughter nuclei. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm and the organelles divide, resulting in each cell being enclosed by its own plasma membrane. The cell cycle is very important to a human's well being. It kicks in to repair injuries, and to help us grow.
The cell that divides is the parent cell, and the daughter cells are the new cells. When mitosis is about to occur, the chromatin in the nucleus becomes condensed. The centrosomes duplicate and then separate forming the poles of the mitotic spindle. There are four phases of mitosis. The first, prophase, visibly indicate that the cell is ready to divide. Spindle fibers begin to appear and the nuclear envelope begins to split apart. The nucleolus disappears. The chromosomes shorten and thicken and spindle fibers attach to the centromeres. In the next phase, metaphase, the spindle occupies where the nucleus was. The chromosomes are at the center, each with two sister chromatids. In anaphase, the third phase, the centromeres divide, followed by the sister chromatids. The diploid chromosomes move toward each pole. Last is telophase which happens when the chromosomes reach the poles. There they once again become chromatin. The spindles disappear and the nuclear envelope reforms. There are now two daughter nuclei. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm and the organelles divide, resulting in each cell being enclosed by its own plasma membrane. The cell cycle is very important to a human's well being. It kicks in to repair injuries, and to help us grow.Meiosis is known as reduction division, involving four daughter cells.
Each daughter cell has half as many chromosomes as the parent cell. The parent cells has 2n, or the diploid number of chromosomes, and the daughter cells have n, the haploid number. When meiosis begins, the chromosomes occur in pairs and are called homologues. The divisions of meiosis are meiosis I and meiosis II. During the first one, the chromosomes line up side by side resulting in four chromatids that stay close together. This is called a synapsis. Following this is interkinesis, immediately followed by meiosis II. The centromeres divide and the sister chromatids become chromosomes that are passed on to daughter nuclei. In the end of this process, all four daughter cells have the n number of chromosomes, containing one chromatid. In humans, these cells mature into gametes, sperm and egg), that will fuse during fertilization. Meiosis is part of sexual reproduction. Meiosis I and II both go through the same four stages of nuclear division as mitosis. In prophase I, the spindle appears and synapsis occurs. The homologous chromosomes line up next to each other. This is when an exchange of genetic material may occur. During metaphase I, the homologous pairs line up by themselves at the equator. The events of these two phases ensure that gametes will not have the same chromosomes and genes. 
Meiosis is significant because it is a part of production of sperm and egg. It keeps the chromosome number the same from generation to generation. Even though both mitosis and meiosis are nuclear divisions, there are several differences between the two. Meiosis requires two nuclear divisions while mitosis requires only one. Meiosis produces four daughter cells, mitosis only two. The daughter cells that result from meiosis are haploid, and the daughter cells following mitosis are diploid. The daughter cells from meiosis are not identical to the parent cell. Mitosis occurs in all tissues during growth and repair. Meiosis occurs only at certain times during the life cycle. Meiosis is part of spermatogenesis and oogenesis, the production of sperm and eggs.
People sometimes are born with too many or too few sex chromosomes. Aout of all autosomal trisomies, only Down syndrome, Trisomy 21, has a good chance of surviving after birth. People with Down syndrome have three copies of chromosome 21. Chances of a woman having a child born with Down syndrome increase rapidly with age. People with Down syndrome have the following characteristics...short stature, flat face, stubby finger, and the so called simian line. Mental retardation is unfortunately an accompanying part of Down syndrome though the severity of it varies greatly.
Turner syndrome is a syndrome in whcich the individual only has an X chromosome.. Adult females with Turner syndrome are short and have a broad chest with folds of skin on the backs of their necks. They do not undergo puberty or menstruate.
Klinefelter syndrome is when a male is born with two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome. The symptoms are very subtle. There may be some delays with speech and language.
A female with more than two X chromosomes have Poly X. Jacobs Syndrome occurs when males have an X chromosome and two Y chromosomes. They are usually of above average height and have speech problems.
Other chromosomal disorders can occur when there is a change to chromosome structure. There are several types of changes that can occur. A deletion is when an end of a chromosome breaks off. A duplication is when a chromosomal segment appears more than once. An inversion is when a segment of the chromosome is turned 180 degrees. A translocation is when a segment moves from one chromosome to another. A deletion can cause a syndrome such as Williams syndrome. Children with this syndrome are said to have the appearance of pixies and have excellent verbal and musical skills.
Cancer envelopes more than a hundred different diseases, but they all have similarities. Cancer cells do not look like any other cells, and they do not contribute to any function in the body. They have enlarged nuclei and may contain more chromosomes. They are immortal and divide an infinite number of times. They pile together and form a tumor. They don't need growth factors and continuously divide. They gradually become abnormal.

Meiosis is significant because it is a part of production of sperm and egg. It keeps the chromosome number the same from generation to generation. Even though both mitosis and meiosis are nuclear divisions, there are several differences between the two. Meiosis requires two nuclear divisions while mitosis requires only one. Meiosis produces four daughter cells, mitosis only two. The daughter cells that result from meiosis are haploid, and the daughter cells following mitosis are diploid. The daughter cells from meiosis are not identical to the parent cell. Mitosis occurs in all tissues during growth and repair. Meiosis occurs only at certain times during the life cycle. Meiosis is part of spermatogenesis and oogenesis, the production of sperm and eggs.
People sometimes are born with too many or too few sex chromosomes. Aout of all autosomal trisomies, only Down syndrome, Trisomy 21, has a good chance of surviving after birth. People with Down syndrome have three copies of chromosome 21. Chances of a woman having a child born with Down syndrome increase rapidly with age. People with Down syndrome have the following characteristics...short stature, flat face, stubby finger, and the so called simian line. Mental retardation is unfortunately an accompanying part of Down syndrome though the severity of it varies greatly.
Turner syndrome is a syndrome in whcich the individual only has an X chromosome.. Adult females with Turner syndrome are short and have a broad chest with folds of skin on the backs of their necks. They do not undergo puberty or menstruate.
Klinefelter syndrome is when a male is born with two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome. The symptoms are very subtle. There may be some delays with speech and language.
A female with more than two X chromosomes have Poly X. Jacobs Syndrome occurs when males have an X chromosome and two Y chromosomes. They are usually of above average height and have speech problems.
Other chromosomal disorders can occur when there is a change to chromosome structure. There are several types of changes that can occur. A deletion is when an end of a chromosome breaks off. A duplication is when a chromosomal segment appears more than once. An inversion is when a segment of the chromosome is turned 180 degrees. A translocation is when a segment moves from one chromosome to another. A deletion can cause a syndrome such as Williams syndrome. Children with this syndrome are said to have the appearance of pixies and have excellent verbal and musical skills.
Cancer envelopes more than a hundred different diseases, but they all have similarities. Cancer cells do not look like any other cells, and they do not contribute to any function in the body. They have enlarged nuclei and may contain more chromosomes. They are immortal and divide an infinite number of times. They pile together and form a tumor. They don't need growth factors and continuously divide. They gradually become abnormal.

picture is of a dividing cancer cell
Cancer is a genetic disease. Oncology is the study of cancer. Oncologists classify cancer according to the place it originates. There are four main types. Carcinomas are of the epithelial tissues. Sarcomas are found in muscles and connective tissue. Leukemias are found in blood. Lymphomas are in the lymphatic tissue. Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer. Another common type is colorectal, or cancer of the colon/rectum. My grandmother was diagnosed with colorectal cancer at the age of 73, and four years later was in remission. Around the age of 81, she was diagnosed with kidney cancer, and again a couple years later was in remission. She will be 85 next month and shows no signs of cancer.
Cancer can be hereditary. It can also be caused by environmental carcinogens such as radiation and organic chemicals. Diagnostic x rays account for most of a person's exposure to artificial radiation. Tobacco smoke and pollutants are very harmful. DNA viruses are also directly believed to cause cancer. Nutrition can help a person prevent cancer.
Seven warning signs can help us become aware of whether we need to be concerned. These can be remembered by the word CAUTION. Change in bowel or bladder habits, A sore that does not heal, Unusual bleeding or discharge, Thickening or lump in breast or elsewhere, Indigestion or difficulty in swallowing, Obvious change in wart or mole, Nagging cough or hoarseness.
There are several tests that can help diagnosis cancer. The earlier a cancer is found, the better the chance for effective treatment. Routine screening tests, by yourself, and by your physician help to detect the presence of cancer early. Tumor marker tests test the blood for tumor antigens and antibodies. Testing for genetic mutations can also help detect cancer.
There are several types of treatment for cancer. Sometimes surgery is effective all by itself, if it is possible to remove the whole tumor. Surgery is usually either preceded or followed by radiation which causes cell cycle disruption. Chemotherapy is a very common treatment which treats the whole body. This treatment interferes with DNA synthesis. There are also quite a few new therapies that are currently in clinical trials. One of the new ideas is to use immune cells that have been genetically engineered to beat the tumor antigens. Another proposed therapy is drugs that inhibit angiogenesis which confine and reduce tumors.
Genetics and the genes we inherit from our relatives play a big part in making us who we are. Genotype are the genes of an individual. Different forms of a gene that have the same position, or locus, on a pair of chromosomes that affect the same trait are called alleles. A dominant allele uses an uppercase letter and a recessive allele uses a lowercase one. If a zygote has a homozygous dominant genotype, that means it would be denoted by using two uppercase letters, such as EE. A homozygous recessive would possibly be ee, and a heterozygous dominant would use one of each, or Ee. A phenotype is the physical appearance of a person. Either a homozygous dominant or a heterozygous dominant would result in the person having the dominant phenotype.
The chromosome number is reduced during the process of gametogenesis. If an individual had the alleles EE, all gametes would have an E. If an individual were Ee, half would carry and E, and the other half an e. If all were ee, the all the gametes would have an e.
A punnett square illustrates when all possible types of sperm are lined up vertically and all possible types of eggs are lined up horizontally. The result is that all possible combination of gametes is shown. This allows you to figure the chances of an individual having certain genotypes or phenotypes.
If a genetic disorder is autosomal dominant, any individual with alleles AA or Aa will end up with the disorder. If the disorder is autosomal recessive, only individuals with aa will have the disorder. It is possible for parents to be carriers and pass a disorder onto their child without actually having the disorder themselves. In reverse, the parents can each have a disorder without passing it on to their child.
One well known autosomal disorders is Tay-Sachs disease, which occurs commonly among Jewish people in the United States. A baby is born appearing to be healthy. Between four and eight months old the child's development slows down and neurological impairment and psychomotor difficulties begin. The child becomes blind and helpless, begins to have seizures, and ends up paralyzed. Another autosomal recessive disorder is Cystic fibrosis which is most lethal in american caucasians. Mucus in the bronchial tubes is very thick interfering with breathing. Huntington disease is a neurological disorder that included progressive degeneration of the cells in the brain. People with this condition deteriorate quickly. I have a client with this disorder that, in the last three years, I have seen the rapid progression, and it is very sad to watch.
There are several other type of inheritance patterns. Skin color and height are regulated by multiple sets of alleles. These are called polygenic traits. Environmental influences contribute to polygenes that cause club foot, schizophrenia, and cleft lip. Blood type is controlled by multiple alleles.
Traits controlled by the genes in the sex chromosomes are considered sex linked. Color blindness is an example of an x-linked trait. Most sex linked disorders are usually on the x chromosome. Muscular dystrophy, and hemophilia are common X linked disorders.
DNA is found mainly in the chromosomes and is our genetic material. Any genetic material has to be able to replicate to transmit to the next generation, store information, and undergo mutations that provide genetic variability.
RNA is made up of nucleotides that contain ribose. Instead of containing the base thymine, RNA contains uracil. RNA is single stranded. There are three types of RNA. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is where proteins are synthesized. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries genetic information from the DNA to the ribosomes. Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers amino acids to the ribosomes.
Proteins are made up of amino acids. They determine the function and the structure of all the cells in our body. The protein hemoglobin is what causes our red blood cells to be red in color.
Gene expression is how the four bases can provide enough combinations to code for 20 amino acids. There are several steps to this process. Transcription is the first phase. First, mRNA is formed and then it has to be processed before it can enter the cytoplasm. The next phase is translation. During this phase, tRNA molecules bring amino acids to ribosomes. There polypeptide synthesis occurs following the steps : initiation, elongation, and termination. DNA contains a triplet code which stands for a specific amino acid. The chromosome in a certain region must decondense in order for a gene to be transcribed in human cells.

During a thirteen year effort, the Human Genome Project figured out the order of the three billion bases A, T, C, and G in our genomes. The investigators deciphered a short sequence of base pairs using sperm DNA. Genome size is suprisingly not proportionate to the number of genes and does not have anything to do with the complexity of the organism. Then the HGP found out how our gene function in cells to create a human being. By comparing genomes, we are able to better understand how species have evolved. The genomes of all vertebrates are remarkably similar. New endeavors in the scientific world include proteomics (the study of the structure, function, and interaction of cellular proteins), and bioinformatics (the application of computer technologies to the study of the genome).
A person's genome can be modified through Ex vivo gene therapy or in vivo gene therapy.
Science now allows us to clone genes. "Cloning is the production of genetically identical copies of DNA, cells, or organisms through an asexual means (Mader, pg458)." Recombinant DNA allows genes to be cloned. A technician needs a vector where the gene of interest will be introduced into a host cell. Plasmids are common uses for vectors.
Biotechnolgy products include bacteria, plants, and animals which have been genetically engineered. Certain genes are introduced into the cells of these living organisms to get them to behave and develop in certain ways. Animal organs can be used instead of human organs in transplant patients.
In addition to the textbook, I used the following sources:
http://www.dartmouth.edu/~cbbc/courses/bio4/bio4-lectures/images/mitosis.JPG
No comments:
Post a Comment