
A. Human Life Cycle
1. Mitosis and Meiosis
B. Male Reproductive System
1. Orgasm in Males
2. Male Gonads
3. Hormonal Regulation
C. Female Reproductive System
1. Genital Tract
2. External Genitals
3. Orgasm in Females
D. Female Hormone Levels
1. Ovarian Cycle : Non Pregnant
2. Estrogen and Progesterone
3. Uterine Cycle :Non Pregnant
4. Fertilization and Pregnancy
E. Control of Reproduction
1. Birth Control Methods
2. Infertility
F. Sexually Transmitted Diseases
1. STDs caused by Viruses
2. STDs caused by Bacteria
II. Development and Aging
A. Fertilization
1. Steps of Fertilization
B. Pre-Embryonic and Embryonic Development
1. Processes of Development
2. Extraembryonic Membranes
3. Stages of Development
C. Fetal Development
1.Events
2. Development of Genitals
D. Pregnancy and Birth
1. Stages of Birth
E. Development after birth
1. Hypothesis of Aging
2. Effect of Age on Body Systems
The reproductive system is very different in males and females. Puberty is the series of events that brings about sexual maturity in humans. The reproductive organs have several different functions. First of all, the testes produce sperm in males, and the ovaries produce eggs in females. Males transport the sperm in ducts and females transport the eggs in the uterine tubes. The male penis delivers sperm to the female vagina. The uterus helps the fertilized egg to develop within a female. The testes and ovaries produce sex hormones that maintain the testes and ovaries and cause masculinization and feminization of several features.
Human DNA is distributed among 46 chromosomes inside the nucleus. Every cell in the human body has that number of chromosomes. When a cell divides by mitosis, or duplication division, the cell produces exact copies of itself. Human cells also can go through another process of division called meiosis, or reduction division. During meiosis, the number is reduced to 23, or the haploid number of chromosomes. Meiosis is the process by which sperm and egg cells are produced. Since the sperm cell has 23 chromosomes, as does the egg, when they combine they become a zygote and have the full 46 chromosomes.
The primary sexual organs, or gonads, are called testes which are within the scrotum. Sperm is produced by the testes and mature in the epididymis. Sperm has to reach maturation in order to swim to an egg. After leaving the epididymis, the sperm enter a vans deferens where they are stored. The vas deferens curve around the bladder and empty out into an ejaculatory duct which enters the urethra. During ejaculation, sperm exits the penis in a fluid called semen. Seminal fluid is made up of secretions from the seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the bulbourethral glands. Each individual component of semen appears to have its own function. Sperm are more viable in basic solutions which is what seminal fluid is. Swimming sperm require energy, which they get from fructose.
The male organ of sexual intercourse is called the penis. It has a long shaft and an enlarged tip. This tip is usually covered by a layer of skin called the foreskin, although some penises are circumcised (removal of foreskin). There is spongy erectile tissue that extends through the penis and contains distensible blood spaces. When a male is aroused, nerves release nitrous oxide which produces cGMP, causing the smooth muscle of incoming arterial walls to relax and the erectile tissue to fill with blood. This causes the penis to become erect. When sexual stimulation intensifies, sperm enters the urethra. Once the seminal fluid is in the urethra, ejaculation occurs which is caused by rhythmic muscle contractions. This is part of a male orgasm. After ejaculation, the penis returns to a flaccid state. There are up to 400 million sperm released during ejaculation.
The testes begin descending during the last two months of fetal development. They form inside the abdominal cavity, but descend down into the scrotal sacs. The scrotum helps to regulate the temperature of the testes by holding them closer to or further away from the body. A testis is composed of lobules which contain seminiferous tubules. This is where spermatogenesis, or production of sperm, occurs. It takes 74 days for sperm do develop from spermatogonia. Spermatozoa, or mature sperm, have three parts - the head, the middle piece, and the tail.
Androgens are the male sex hormones. They are secreted by cells between the seminiferous tubules. This is why they are called interstitial cells. The most important androgen is testosterone.
The hypothalamus secretes the hormone gonadotropin releasing hormone, which controls the testes' sexual function. There are two different GRHs - follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone. These are present in males and females. Testosterone brings about the male secondary sex characteristics that appear during puberty. Some of these characteristics are taller height, broader shoulders, and deeper voices. Testosterone is also what causes greater muscle development.
Ovaries are the female gonads. They lie on each side of the upper pelvic cavity and produce eggs, along with the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. The oviducts, which are more commonly known as the fallopian tubes, extend from the uterus to the ovaries. They end in fingerlike projections called fimbriae. When an egg bursts from the ovary, it is swept into an oviduct by both the fimbirae and the cilia that lines the oviducts. When the egg is in the oviduct is is propelled toward the uterus by muscle contraction and ciliary movement. Unless it is fertilized, and egg only lives 6-24 hours. When an egg is fertilized it becomes a zygote. In several days, a developing embryo arrives at the uterus and begins implantation. The uterus is the size and shape of an upside down pear. The oviducts join with the uterus at its upper end and the cervix is at its lower end and enters the vagina.
Development of the embryo and the fetus takes place in the uterus, or the womb. The endometrium is the lining of the uterus and participates in forming the placenta. There is a small opening in the cervix leading to the vaginal canal. The vagina acts as an exit for urine and menstrual flow and is the female sexual organ.
The vulva are the external female genitals. They include two large folds of skin called the labia majora. The labia minora are the two smaller folds. The vagina starts out with a ring of tissue called the hymen protecting it. The hymen is ruptured by sexual intercourse or other physical activities.
During stimulation, the labia minora, vaginal wall, and clitoris become engorged with blood. During this time the vagina expands and elongates. Mucus secreting glands provide lubrication for entry of the penis. At the height of stimulation, orgasm occurs.

Ovaries contain many follicles, each one containing an immature egg, or oocyte. Females are born with up to two million follicles, but by puberty that number has dropped to 3 0r 4 hundred thousand. Only about 400 follicles ever reach maturity. The ovarian cycle is when the follicle matures. It changes from a primary to a secondary to a vesicular follicle. Females usually only produce one egg per month. An oocyte undergoes meiosis I. The secondary oocyte undergoes meiosis II if it is fertilized by a sperm cell. When it is time, the vesicular follicle bursts, releasing the oocyte in a process called ovulation. The ovaries provide eggs and the sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. The hypothalamus has complete control of the sexual function of the ovaries through its secretion of GnRH.
Estrogen is responsible for body hair and fat distribution as well as other secondary sex characteristics. Also, the pelvic girdle is wider and deeper in females. The period in a woman's life during which this whole cycle ceases is called menopause. This usually occurs between the ages of 45 and 55. Estrogen and progesterone affect the endometrium which causes the uterus to undergo a 28 day series of events known as the uterine cycle. During the first 5 days, the hormone levels are low, causing the endometrium to disintegrate and the blood vessels to rupture. This is when menstruation occurs. During days 6-13, increased production of estrogen by a new ovarian follicle causes the endometrium to thicken. This is called the proliferative phase. On the 14th day, ovulation usually occurs. During the last half of the cycle, progesterone production increases and the endometrium triples in thickness preparing to receive a developing embryo.

After unprotected sexual intercourse, sperm will make there way into the oviduct. Once a sperm (only one) fertilizes the egg it becomes a zygote. This begins pregnancy. The placenta originates from maternal and fetal tissues. This is the region where exchange of molecules between maternal and fetal blood occurs. The placenta begins to produce human chorionic gonadotropin, or HCG. A pregnancy tests for this hormone. Then the placenta produces progesterone as well as some estrogen.
Birth control pills are taken to help prevent pregnancy from occurring. They are taken for 21 days and contain synthetic sex hormones. After that 7 days of inactive pills are taken. These hormones feed back and inhibit the hypothalamus and the anterior pituitary. They also thicken cervical mucus, preventing sperm from entering.
There are several means of birth control used to try to prevent pregnancy. Abstinence, or refraining from intercourse, is the only foolproof method. Contraceptives are medications and devices that reduce the risk of pregnancy. Oral contraceptives are pills. Another method is an intrauterine device which is a small piece of molded plastic that a physician inserts into the uterus. A diaphragm is a soft latex cup that lodges behind the pubic bone and fits over the cervix. Barrier methods include female and male condoms. Injections and vaccines are also available.
There are more permanent methods of contraceptives. Vasectomy consists of cutting and sealing the vas deferens so that sperm cannot reach the seminal fluid. Tubal ligation is when the oviducts are cut and sealed.
There is a new pill out called a morning after pill which is considered an emergency contraceptive. This contains synthetic progesterone which disrupts the uterine cycle and makes it difficult for an embryo to implant.
The failure of a couple to achieve pregnancy after regular, unprotected intercourse is called infertility. Approximately 15% of all couples are infertile. The most common cause of this is low sperm count in the male. A sedentary lifestyle is the most common cause of male infertility. Body weight is the most significant factor in female infertility.
There are many assisted reproductive technologies available for infertile couples today. Artificial insemination by donor is when sperm is placed in the vagina by a physician. Normally the sperm is from an anonymous donor. In vitro fertilization is when conception occurs in laboratory glassware. Immature eggs are retrieved by a needle and brought to maturity before concentrated sperm is added. After 2-4 days they are transferred to the uterus of the woman. Gamete intrafallopian transfer is when the egg and sperm are immediately placed in the oviducts after being brought together. In some instances, woman are paid by other women to have their babies. There is one last technology called intracytoplasmic sperm injection where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg.
There are several types of sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs. These are caused by viruses, bacteria, protists, fungi, and animals. There is effective treatment available for AIDS and genital herpes, which are caused by viruses. AIDS is the last stage of an HIV infection. There is no cure, but a treatment called highly active antiretroviral therapy is able to stop HIV reproduction to where it is not detectable in the blood. Human papillomaviruses are the cause of genital warts. Genital herpes is caused by herpes simplex virus. Symptoms can include tingling or itching sensation before blisters appear on the genitals. Hepatitis is an infection in the liver and can lead to death.
STDs that are caused by bacteria are curable with antibiotics. Chlamydia is usually mild in women. Men may feel a mild burning sensation during urination. Gonnorhea's symptoms include pain upon urination, and a thick greenish yellow discharge. It can also cause infertility in males. If a baby is exposed during birth, they may develop an eye infection leading to blindness. This is why all newborns are given eyedrops. Syphilis has three stages. During the primary stage, a chancre shows the site of the infection. The secondary stage is when the victim develops a rash and hair loss may occur. The tertiary stage lasts until death.
Sperm have a tail called a flagellum which allows it to swim. The plasma membrane of the egg is surrounded by the zona pellucida. The cells surrounding this area are called the corona radiata. During fertilization, several sperm attempt to penetrate the corona radiata. When a sperm head binds to the zona pellucida, digestive enzymes are released forging a pathway for the sperm. When the sperm binds to the egg, their plasma membranes fuse.
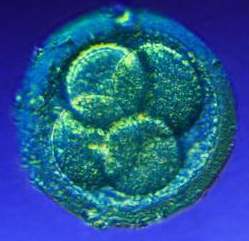
As a human being develops, four separate stages occur. The first stage is cleavage. Immediately after fertilization, the zygote divides creating multiple cells while not growing in size. The second stage is growth, in which the daughter cells begin to increase in size. Next is morphogenesis, or the shaping of the embryo. Differentiation is the stage when the cells take on a specific structure and function.
Extraembryonic membranes are not a part of the embryo. There are several functions of the extraembryonic membranes. The chorion develops into the fetal half of the placenta. The allantois extends away from the embryo and accumulates the urine produced by fetal kidneys. The yolk sac is the first of the embryonic membranes to appear. It contains food for the developing embryo. The amnion enlarges as the embryo enlarges, containing fluid for protection. The stages of development include fertilization through birth. Preembryonic development includes the first week. Following fertilization, the zygote repeatedly divides as it passes into the uterus. A blastocyst is a compact ball of embryonic cells. Each cell within the cell mass has the capability of becoming any type of tissue. Occasionally, the cells of the morula separate, forming twins.
Embryonic development encompasses the second week through the end of the second month of development. At the end of the first week, the embryo implants itself in the uterine wall. Occasionally, an embryo implants itself elsewhere, causing an ectopic pregnancy. This type of pregnancy is not successful. During the time of implantation, the chorion secretes enzymes that digest some of the tissue and blood vessels of the uterus. It also begins to secrete human chorionic gonadotropin. During this second week, the inner cell mass becomes the embryonic disk and the yolk sac and amniotic cavity form. During the major event of gastrulation, the inner cell mass becomes the embryonic disk. During the third week of development, the nervous system becomes the first organ system to be visually evident. A thickening appears along the entire length. The neural folds meet at the midline and the neural tube is formed. Development of the heart also begins this week. At four weeks, the embryo is only about a quarter of an inch in size. A body stalk connects the embryo to the chorion. The head and the tail lift up. The umbilical cord forms. Limb buds begin to appear and the head enlarges. The sense organs become visible. Between the sixth and eighth week of development, the embryo changes into a form recognizable as a human. The nervous system begins to develop reflex actions.

At the end of eight weeks the embryo is 1.5 inches long and weighs about the same as an aspirin tablet.
The placenta is where progesterone and estrogen are produced during pregnancy. They prevent any new follicles from maturing and they maintain the endometrium. The placenta's fetal side is contributed by the chorion and the maternal side consists of uterine tissues. The umbilical cord contains the umbilical arteries and vein. The arteries carry oxygen poor blood to the placenta. The vein carries blood that is rich in nutrients and oxygen away from the placenta to the fetus.
The third through ninth months of development are known as fetal development. Head growth begins to slow down during the third month. Fingernails, nipples, eyelashes, eyebrows, and hair appear. Cartilage is slowly replaced by bone. Sometime during the third month males are distinguishable from females.
During the fourth month, the fetal heartbeat can be heard by placing a stethoscope on the mother's abdomen. At the end of this month the fetus is about 6 inches long and weighs about 6 ounces.
The mother begins to feel movement sometime during the fifth and seventh months. During this time the wrinkled skin is covered by a fine down called lanugo which is coated with a white, cheeselike substance called vernix caseosa.

The eyelids are open during this time. At the end of the seventh month, the fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs about 3 pounds. If the fetus was born now, it is possible to survive.
At the end of nine months the fetus is about 20.5 inches long and weighs about 7.5 pounds. The fetus usually rotates during the end of development so that its head is pointed toward the cervix to prepare for birth. If the fetus does not turn and is rump down, a breech birth is likely to occur. This makes it difficult for the cervix to expand and a cesarean section may be how the baby needs to be delivered.
The sex of a person is determined as soon as fertilization occurs. Males have XY chromosomes and females have XX chromosomes. It is impossible to tell just by inspection whether an unborn child is a boy or a girl during the first several weeks of development. Gonads begin developing during the seventh week. At 14 weeks, the primitive testes and ovaries are located deep inside the abdominal cavity. At fourteen weeks the urogenital groove has disappeared in males and the scrotum forms. In females, the groove persists and becomes the opening for the vagina.
The absence of one or more of the sex hormones causes ambiguous sex determination. In this case, the person has the external appearance of a female but the gonads are absent. In androgen insensitivity syndrome, the individual develops as a female because the receptors for testosterone are ineffective and the external genitalia develop as a female. However, the individual has testes inside the body.
When a woman first becomes pregnant, she may experience nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, and fatigue. These symptoms usually subside and the mother has a period of increased energy levels. Weight gain is caused due to breast and uterine enlargement, weight of the fetus, amniotic fluid, the size of the placenta, and other factors. The increased weight can cause lower back pain.

myself at 7 months pregnant
The arteries in the uterus expand and this leads to low blood pressure. An increase in the number of red blood cells follows and cardiac output increases by 20-30%. The uterus ends up occupying most of the abdominal cavity. Compression of the ureters and urinary bladder can result in stress incontinence. Compression of the inferior vena cava can result in edema and varicose veins. Stretch marks, or striae gravidarum typically appear over the abdomen and lower breasts as a result of stretching of the skin.
Throughout pregnancy, the uterus has contractions. Near the end of pregnancy, contractions become stronger and more frequent. False labor contractions are called Braxton Hicks contractions. The onset of true labor is contractions that occur regularly every 15-20 minutes and last for at least 40 seconds. Parturition is the process of giving birth to an offspring. Prior to the first stage, there can be what is known as a "bloody show" which is caused by the expulsion of a mucous plug from the cervical canal.
During the first stage of labor, the uterine contractions occur and the cervical canal slowly disappears. The lower part of the uterus is pulled toward the baby's head. This is called effacement. If the amniotic membrane has not ruptured, it may do so during this phase. Stage one ends when the cervix is completely dilated.
During stage 2, the uterine contractions occur every 1-2 minutes and last for about a minute. This is accompanied by a desire to push. As the baby's head descends it turns so that the back of the head is uppermost. An episiotomy is sometimes performed to enlarge the vaginal orifice. Once the head is delivered, the physician holds the head and guides it downward until the rest of the baby is out. Once the baby is breathing normally the umbilical cord is cut.
The third stage is when the placenta, called the afterbirth is delivered.
Development does not end at birth. It continues throughout our lives during infancy, childhood, adolescence, and adulthood. Aging is the progressive changes that contribute to an increased risk of infirmity, disease, and death. Gerontology is the study of aging. The number of people over the age of 65 will increase 147% in the next half of a century. The human life span is a maximum of 120-125 years.
There are three hypotheses of aging. Several researchers believe that aging has a strong genetic basis. They have worked with roundworms and found many genes whose expression decreases life span. Another theory contains a whole body process; This is due to a decline in the hormonal system which affects many organs of the body. Some of the diseases and problems seen in older humans include diabetes type 2, menopause, and many other things. The immune system does not perform as well as a person gets older. Extrinsic factors are another theory for aging. This states basically that how we take care of ourselves affects how well our bodies will function as we get older.
Age effects many different body systems in many ways. Skin becomes thinner and less elastic. This loss of thickness causes some of the sagging and wrinkling of the skin. There are fewer sweat glands making homeostatic adjustment to heat limited. Oil glands are also fewer, causing skin to crack.
The leading cause of death today is cardiovascular disorders. The heart begins to shrink during aging. Blood flow to the liver is reduced, and the liver does not metabolize drugs very efficiently. Blood supply is also reduced to the kidneys. The digestive tract begins to lose tone, and there is a reduction of saliva and gastric juice. However, few neural cells of the cerebral cortex are lost. Cognitive skills remain unchanged. Reaction time slows. Loss of skeletal mass is common, but can be controlled by exercise. Females undergo menopause. Males undergo andropause. Females on average live longer than males.
Aging is inevitable, but by developing health habits now, we can prepare for successful old age.

4 generations - ages 2 through 85
Images are from these sites:
3 comments:
Thank you! Your help is appreciated, Very very interesting article. Thanks for collecting and providing so much info. I am a 54 year old man and I had problems of erectile dysfunction but it already was a stage closed in my life but I find the solution, I bought Online Viagra the Online Pharmacy is the best option to buy Viagra you only must go to the computer and ready!!
very informative nice and interesting blog thanks for sharing this post here i love to share about tubal reversal>Tubal Reversal is a process for those women who would like to restore their fertility in order to have more babies.
great and awesome reproductive blog...i am really impressed to see it...
I recently see a site mybabydoc.com of an very experienced doctor name as DR Morice and specialized in woman issues like Fertility, Tubal Ligation Reversal,treatment,Cosmetic Surgery,vaginal tightness and much more like these..
Post a Comment